


They are otherwise called routine decisions or structured decisions. Some of the decisions are discussed below: Types of Decision Making – 17 Important Types of Decisions Groups or collective decisions refer to the decisions which are taken by a group of organisational members, say Board of Directors or a Committee. Such decisions are generally taken in small organisations and in those organisations where autocratic style of management prevails. When a decision is taken by an individual in the organisation, it is known as individual decision. There has to be adequate probing and analysis of various alternatives before taking such decisions. Non-programmed decisions require thorough study of the problem and scientific analysis of the situational factors. It has to be dealt with an unstructured problem and the decision should be taken by the chief executive. He can deal with such an employee according to the standard procedure which may include charge sheet, suspension, etc.īut if a large number of employees absent themselves from work without any intimation, such a problem cannot be dealt in a routine manner. For instance, if an employee absents himself from his work for a long time without any intimation, the supervisor need not refer this matter to the chief executive. There is no standard procedure for handling such problems. But the non-programmed decisions arise because of unstructured problems. The programmed decisions are of a routine and repetitive nature which are to be dealt with according to specific procedures. But personal decisions, which relate to the manager as an individual and not as a member of the organisation, cannot be delegated. Organisational decisions are those which a manager takes in his official capacity. For instance, the bonus issue is a policy matter which is to be decided by the top management, and calculation of bonus is an operating decision which is taken at the lower levels to execute the policy decision. But operating decisions are taken by the lower management in order to put into action the policy decisions. Policy decisions are of vital importance and are taken by the top management. The managers are more serious about such decisions as they influence decision-making at the lower levels. Finding the correct problem in such decisions assumes great importance. The strategic decisions relate to policy matters and so require a thorough fact finding and analysis of the possible alternatives. The higher the level of a manager, the more strategic decisions he is required to take. Strategic or basic decisions, on the other hand, are more important and so they are taken generally by the top management and middle management. Such decisions are generally taken by the managers at the middle and lower management level. They do not require any special effort by the manager. They may be complicated but are always one-dimensional. Thus, they can be taken without much deliberation. They neither require collection of new data nor conferring with people. Tactical or routine decisions are made repetitively following certain established rules, procedures and policies. Types of Decision Making – Routine, Strategic, Policy, Operating, Organisational, Personal, Programmed, Non-Programmed, Individual and Group Decisionsĭecisions may be classified according to different bases which are discussed below: Type # 1. Group decision making is preferred these days because it contributes for better coordination among the people concerned with the implementation the decision. Individual decisions are taken where the problem is of routine nature, whereas important and strategic decisions which have a bearing on many aspects of the organization are generally taken by a group. For example: the manager’s decision to quit the organization, though personal in nature, may create some problems for the organization.
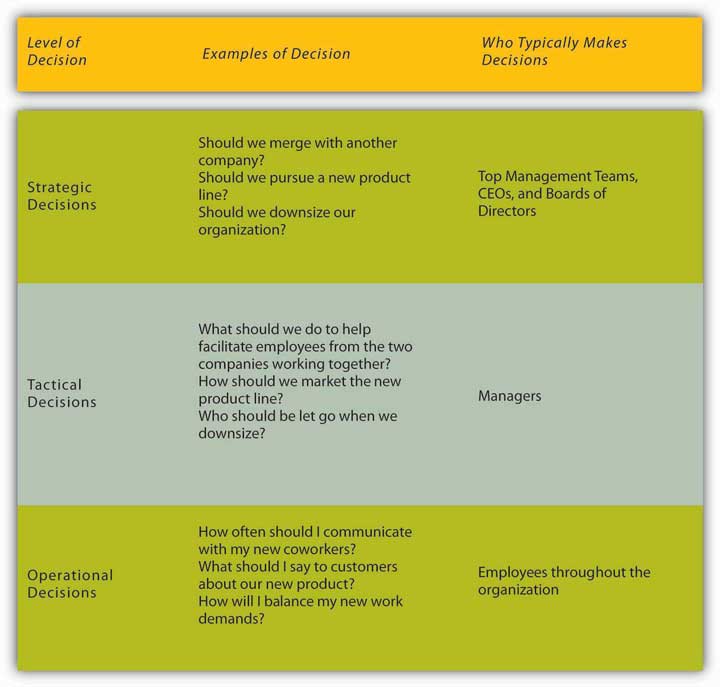
However, their impact may affect the organization also. On the other hand, managers do take some decisions which are purely personal in nature. are taken by managers to achieve certain objectives. For example: decisions regarding introducing a new incentive system, transferring an employee, reallocation or redeployment of employees etc. Organizational and Personal Decisions:ĭecisions taken by managers in the ordinary course of business in their capacity as managers are organizational decisions. The focus in the operational decisions is on the short-run or immediate present, while it is on the long- rum in the case of strategic decisions.ģ. Usually, routine decisions are taken by managers at the lower levels, while strategic decisions are taken by top level managers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
